in this guest post, Najwa Whistler offers some insights into preventing and detecting fraud in beneficiary distribution lists. Experiences have been anonymised. Images are used for illustration only, and there is no suggestion that the events shown involved any of the issues discussed in Najwa’s article.

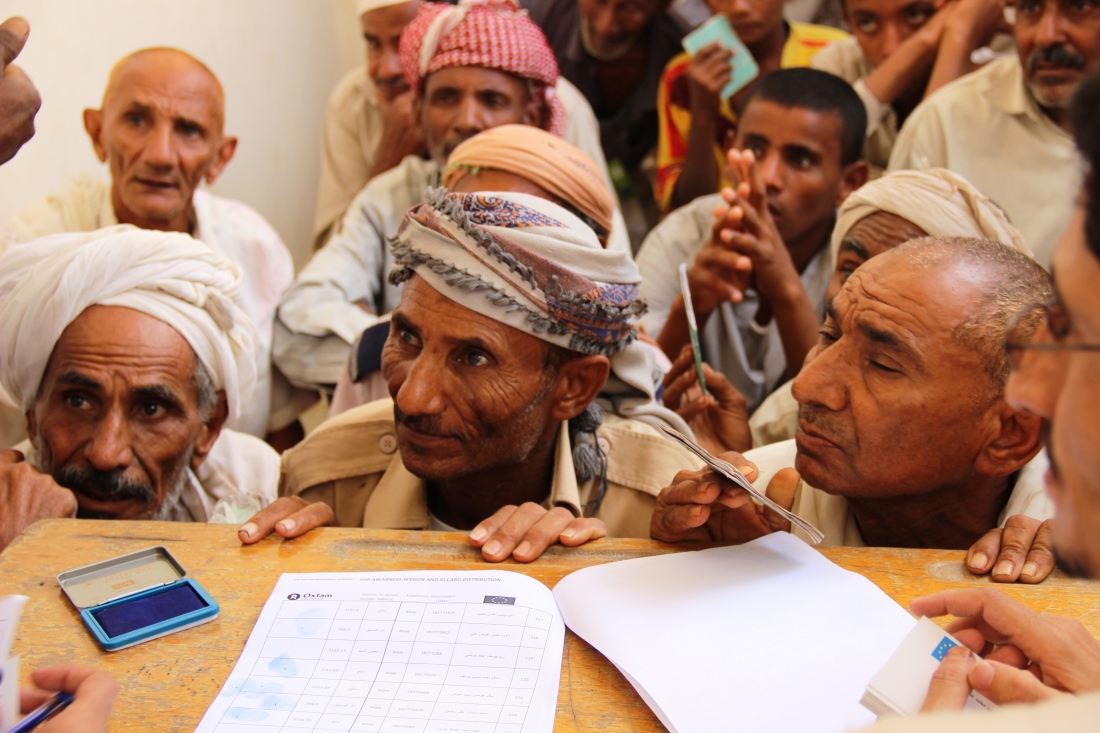
A common form of evidence that a distribution of food or Non-Food Items (NFIs, such as hygiene kits), a training event, or any other service actually took place is a list of named recipients. This might be either pre-printed or handwritten, and featuring the signature or fingerprint of the recipients. In principle this should work – but does it work in practice?
From the experience of my colleagues and I in different NGOs, in both emergency and non-emergency contexts, here are some real-life examples.
One organisation was distributing NFIs in a very insecure location to the most vulnerable population. The organisation relied on its local staff for the distribution, beneficiaries were asked for a fingerprint as the unique identifier of receipt, and the senior managers were satisfied upon receipt of all the distribution lists. But when an audit was conducted by the donor, the auditors became concerned about the lists and sent them to a forensic laboratory. The results came back that all the prints belonging to just five individuals, and not all were finger prints. I couldn’t remove the image from my head of someone dipping their toes in ink!
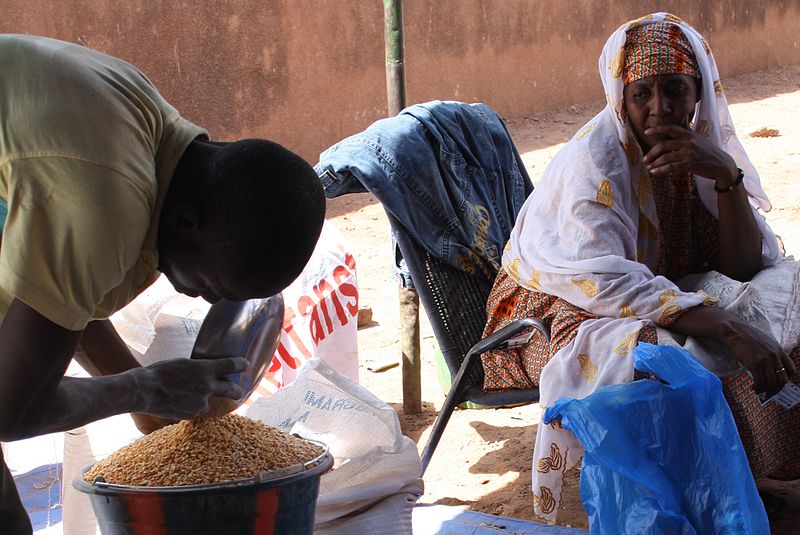

While the organisation went the extra mile to reach the unreachable and ensure no beneficiary was left behind, five people were going the extra mile to spend hours faking records to steal from them.
Another example is when these records come back crisp, clean and as good as new. You can be almost sure that the papers have never left the desk of the supervisor. Other things to watch out for closely are signatures that are easily recognised as being signed by the same person, signatures with repetitive recipient names, or family names that alternate with first names.
Of course, these red flags do not necessarily mean fraud has taken place. Sometimes, for example, one person signs on behalf of other beneficiaries because they couldn’t all travel to the point of distribution. Or maybe the supervisor signs on behalf of the beneficiaries because it is not practical to collect a signature or fingerprint during the distribution. These situations are different to the creation of phantom beneficiaries, or falsely confirming that a service or item has been delivered.
What can we do about it?
In acute emergencies, the efforts should be focused on reaching people, eliminating their suffering, and treating them with dignity and respect. Collecting recipients’ confirmation can be impractical at times.
 In these situations, organisations can rely on alternative evidence of the delivery, such as the evidence of the supplies’ transport to, and arrival at, the point of distribution. Distributions can also be recorded with modern technologies such as biometrics, body cameras on the distributors, or even mini-drones which can be deployed to record at a set altitude above a person wearing a transmitter.
In these situations, organisations can rely on alternative evidence of the delivery, such as the evidence of the supplies’ transport to, and arrival at, the point of distribution. Distributions can also be recorded with modern technologies such as biometrics, body cameras on the distributors, or even mini-drones which can be deployed to record at a set altitude above a person wearing a transmitter.
Organisations can also consider:
- Conducting individual interviews with the staff involved in the distribution. Don’t exclude drivers and guards. They can be good witnesses, giving their experience of the distribution to enable organisations to compare stories for any inconsistencies or reasons for suspicion;
- Keeping photographs and videos from cell phones if no other technology is available;
- Ensuring that the delivery team is from different departments in the organisation, where possible;
- Ensuring that emergency response personnel are trained on the counter-fraud, anti-corruption and whistleblowing policies that the organisation has in place.
 In non-emergency activities such as training, incorporating fraud detection into post-event monitoring and evaluation is key. Organisations can randomly select a sample of recipients, contact them for feedback, and verify receipt of the items or service.
In non-emergency activities such as training, incorporating fraud detection into post-event monitoring and evaluation is key. Organisations can randomly select a sample of recipients, contact them for feedback, and verify receipt of the items or service.
Monitoring questions of a training delivery might be:
- Your name?
- Did you receive any training in the last 6 months?
- Who was the provider?
- Where was the training?
- What was the subject of the training?
- What session did you find most useful?
- How did the training that you’ve received helped you improve in your daily work?
- Who else attended the training?
- How do you rate the trainer’s skills?
- Give one recommendation to improve future trainings, what can be done differently?
- What is your feedback on the venue? Was lunch provided? Did you receive a per-diem or transport cost? How much did you receive?
- Any comments/other feedback?
In summary, these days technology has made monitoring and evaluation much easier and more efficient. But even so, we must be careful not to exchange one set of risks for another. The key to successful prevention and detection of fraud in beneficiary lists is to think creatively, both about how we apply controls in difficult circumstances – and how we catch those who collude to overcome them.
 Najwa Whistler is a finance director with 18 years of experience working for several international NGOs around the world. Growing up in a small village in Lebanon in poverty during the civil war built her resilience and determination to work in international development. She enjoys cooking and dancing. You can reach her via naj.whistler@gmail.com
Najwa Whistler is a finance director with 18 years of experience working for several international NGOs around the world. Growing up in a small village in Lebanon in poverty during the civil war built her resilience and determination to work in international development. She enjoys cooking and dancing. You can reach her via naj.whistler@gmail.com
Cover photo: During the crisis in Yemen, ECHO funded a second phase of a cash distribution programme to help 4,000 families meet their basic needs during the pre-harvest lean season between July and December 2012. Close monitoring ensured that money was spent on essential items (ECHO/T. Bertouille, 2012).



 There is a disconnect between the perception of reputational risk and the action taken to manage it.
There is a disconnect between the perception of reputational risk and the action taken to manage it. One of the report’s most surprising findings was the under-use of risk assessment. This might not surprise NGOs, however; my counter-fraud colleagues and I have found the quality and extent of risk assessment in the sector to be patchy at best.
One of the report’s most surprising findings was the under-use of risk assessment. This might not surprise NGOs, however; my counter-fraud colleagues and I have found the quality and extent of risk assessment in the sector to be patchy at best. The biggest proportion of incidents reported were conflicts of interest, with personal favours not far behind. This may resonate with NGO managers; anecdotally, conflicts of interest in procurement and recruitment can be a real issue.
The biggest proportion of incidents reported were conflicts of interest, with personal favours not far behind. This may resonate with NGO managers; anecdotally, conflicts of interest in procurement and recruitment can be a real issue. Respondents most frequently declared organisational culture and tone-at-the-top as the greatest preventative factors. I have written about the link between culture and corruption for NGOs before (
Respondents most frequently declared organisational culture and tone-at-the-top as the greatest preventative factors. I have written about the link between culture and corruption for NGOs before ( To read more about how to deter, prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption in humanitarian and global development work, make sure you pick up a copy of my book,
To read more about how to deter, prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption in humanitarian and global development work, make sure you pick up a copy of my book, 
 If a humanitarian or global development organisation gets serious about tackling fraud and corruption, then it will detect cases – possibly in significant numbers. As my organisation invested in counter-fraud efforts, for example, we saw recorded suspicions in its global operations
If a humanitarian or global development organisation gets serious about tackling fraud and corruption, then it will detect cases – possibly in significant numbers. As my organisation invested in counter-fraud efforts, for example, we saw recorded suspicions in its global operations  The job does not finish with the dismissal or conviction of the suspect(s). These incidents have long tails – there is work still to be done to rehabilitate the project or business unit in which the incident took place. An incident represents a severe breach of trust; workers may feel abused and betrayed. The ripples can spread wide.
The job does not finish with the dismissal or conviction of the suspect(s). These incidents have long tails – there is work still to be done to rehabilitate the project or business unit in which the incident took place. An incident represents a severe breach of trust; workers may feel abused and betrayed. The ripples can spread wide. Hopefully, the organisational response included a lessons-learned exercise, generating changes to implement. This should look beyond the internal controls, also into enabling factors such as culture, communication and awareness.
Hopefully, the organisational response included a lessons-learned exercise, generating changes to implement. This should look beyond the internal controls, also into enabling factors such as culture, communication and awareness. Now is also a good time to do some contingency planning. Is the incident serious enough that it could result in regulatory interest, onerous remedial controls applied by institutional donors, or put future funding at risk, for example? We can prepare for these.
Now is also a good time to do some contingency planning. Is the incident serious enough that it could result in regulatory interest, onerous remedial controls applied by institutional donors, or put future funding at risk, for example? We can prepare for these.
 Team members will respond to the matter differently. While some may be relatively unaffected, others may not. It is important to note that where staff have made a commitment to an organisation on the basis of their values – perhaps more common for charities, nonprofits and NGOs than for private sector organisations – a breach of trust could be more impactive. Perhaps there could even be a grief reaction for some team members.
Team members will respond to the matter differently. While some may be relatively unaffected, others may not. It is important to note that where staff have made a commitment to an organisation on the basis of their values – perhaps more common for charities, nonprofits and NGOs than for private sector organisations – a breach of trust could be more impactive. Perhaps there could even be a grief reaction for some team members. Look out for, and respond to, the traditional symptoms of stress, low morale and anxiety. These might include absenteeism, disciplinary issues, a rise in complaints, and disillusionment. An incident can impact upon personal and professional confidence, and colleagues may feel fear, shame or embarrassment. Will the incident create a funding crisis, putting their jobs at risk? Will staff have to justify themselves to an angry public? Consider access to staff support systems, and formal interventions such as counselling and facilitated debriefing.
Look out for, and respond to, the traditional symptoms of stress, low morale and anxiety. These might include absenteeism, disciplinary issues, a rise in complaints, and disillusionment. An incident can impact upon personal and professional confidence, and colleagues may feel fear, shame or embarrassment. Will the incident create a funding crisis, putting their jobs at risk? Will staff have to justify themselves to an angry public? Consider access to staff support systems, and formal interventions such as counselling and facilitated debriefing. Be a compassionate and responsive manager. Avoid assuming you understand how people feel or why they behave the way they do. Instead, in your one-to-one meetings with team members, explore how they are experiencing the crisis and responding to it. Remember, of course, to make it clear that this is pastoral and not investigative. Similarly, it is important to restore individuals’ sense of control. In a way, employees in whose midst an act of fraud or corruption occurred are victims of abuse. Solicit and listen to their concerns and visibly respond to them.
Be a compassionate and responsive manager. Avoid assuming you understand how people feel or why they behave the way they do. Instead, in your one-to-one meetings with team members, explore how they are experiencing the crisis and responding to it. Remember, of course, to make it clear that this is pastoral and not investigative. Similarly, it is important to restore individuals’ sense of control. In a way, employees in whose midst an act of fraud or corruption occurred are victims of abuse. Solicit and listen to their concerns and visibly respond to them. Clear communication. Rebuilding trust requires the open communication of reliable content. Low information creates anxiety, more information helps manage our ‘fight or flight’ crisis response. Concealing the matter from the team is, therefore, more likely to sow suspicion and fear than peace and confidence. Be as open as you can about what has happened, and what will now happen, within the boundaries of policy, employment law and data protection legislation. As you describe the future, avoid over-promising – employees need clear and consistent messaging from management. If you cannot make promises, don’t; recognise uncertainty and explain what is being done to reduce it.
Clear communication. Rebuilding trust requires the open communication of reliable content. Low information creates anxiety, more information helps manage our ‘fight or flight’ crisis response. Concealing the matter from the team is, therefore, more likely to sow suspicion and fear than peace and confidence. Be as open as you can about what has happened, and what will now happen, within the boundaries of policy, employment law and data protection legislation. As you describe the future, avoid over-promising – employees need clear and consistent messaging from management. If you cannot make promises, don’t; recognise uncertainty and explain what is being done to reduce it. Foster trusting relationships. Ensure that teams meet as regularly as possible, in person or via teleconferencing. Consider holding team-building events, reflective away days and/or ‘how are we doing’ agenda items in meetings. These measures can improve understanding, interaction and trust between team members.
Foster trusting relationships. Ensure that teams meet as regularly as possible, in person or via teleconferencing. Consider holding team-building events, reflective away days and/or ‘how are we doing’ agenda items in meetings. These measures can improve understanding, interaction and trust between team members. Lead by example. We know that employees look to the behaviour of their managers to determine their own. So be present; you cannot role-model behaviours and attitudes if you cannot be seen by anyone. Be positive and show how you treat what has happened constructively, managing risk, avoiding blame, taking care of your colleagues (and yourself), and using the incident to make the business unit stronger in the future. As one casualty of a fraud or corruption incident is honesty, ensure that you are (and are seen to be) authentic. So, for example, if you feel hurt, vulnerable or confused, consider sharing those feelings with the team. This helps to normalise these emotions.
Lead by example. We know that employees look to the behaviour of their managers to determine their own. So be present; you cannot role-model behaviours and attitudes if you cannot be seen by anyone. Be positive and show how you treat what has happened constructively, managing risk, avoiding blame, taking care of your colleagues (and yourself), and using the incident to make the business unit stronger in the future. As one casualty of a fraud or corruption incident is honesty, ensure that you are (and are seen to be) authentic. So, for example, if you feel hurt, vulnerable or confused, consider sharing those feelings with the team. This helps to normalise these emotions. Reaching project milestones or completing tasks puts clear blue water between the incident and the present, assisting both staff and stakeholders to move on. It also, of course, ensures the progress of the project or business unit. Embed, as rapidly and effectively as possible, any changes to processes to reduce the risk of a recurrence.
Reaching project milestones or completing tasks puts clear blue water between the incident and the present, assisting both staff and stakeholders to move on. It also, of course, ensures the progress of the project or business unit. Embed, as rapidly and effectively as possible, any changes to processes to reduce the risk of a recurrence. To read more about how to deter, prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption in humanitarian and global development work, make sure you pick up a copy of my book,
To read more about how to deter, prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption in humanitarian and global development work, make sure you pick up a copy of my book, 


 Fraud and corruption has, historically, not been well understood in this sector. Your Board may have a low or rudimentary understanding of the risk and how to respond to it. This means starting at a basic level, making no assumptions, taking the time to address myths and misconceptions and playing a longer game. ‘Educate as you go,’ Willie Oelofse from Deloitte Kenya told NGOs at
Fraud and corruption has, historically, not been well understood in this sector. Your Board may have a low or rudimentary understanding of the risk and how to respond to it. This means starting at a basic level, making no assumptions, taking the time to address myths and misconceptions and playing a longer game. ‘Educate as you go,’ Willie Oelofse from Deloitte Kenya told NGOs at 
 Civil society is under attack the world over, and the issue of their fraud and corruption exposure can be something that sends Board members running for their shields and helmets – especially if it is perceived to come from an
Civil society is under attack the world over, and the issue of their fraud and corruption exposure can be something that sends Board members running for their shields and helmets – especially if it is perceived to come from an  Fraud and corruption, especially at a strategic level, can be abstract concepts. Help the Board to connect by painting a picture of the risk with case studies. If you don’t have any in your own organisation, then perhaps partners, donors or other organisations have some they will let you use? If not, then find cases in the public space affecting comparable organisations. If you’re really struggling, consider using fictional examples – but remember to state that they’re fictional!
Fraud and corruption, especially at a strategic level, can be abstract concepts. Help the Board to connect by painting a picture of the risk with case studies. If you don’t have any in your own organisation, then perhaps partners, donors or other organisations have some they will let you use? If not, then find cases in the public space affecting comparable organisations. If you’re really struggling, consider using fictional examples – but remember to state that they’re fictional! NGO Boards are often allergic to anything with a whiff of extra expense, especially if it is
NGO Boards are often allergic to anything with a whiff of extra expense, especially if it is  NGO Boards manage a lot of risks, only some of which materialize. Using evidence helps them to appreciate how fraud and corruption sits, whether that evidence is perception-based, representative sampled, or from other diverse sources. Cast the evidence net wide – consider staff surveys (especially anonymous surveys), risk assessments, project and programme evaluations, audit reports, security reports, academic research and open source. This may mean that you need to start by
NGO Boards manage a lot of risks, only some of which materialize. Using evidence helps them to appreciate how fraud and corruption sits, whether that evidence is perception-based, representative sampled, or from other diverse sources. Cast the evidence net wide – consider staff surveys (especially anonymous surveys), risk assessments, project and programme evaluations, audit reports, security reports, academic research and open source. This may mean that you need to start by  Just as is the case with private and public sector organisations, the counter-fraud agenda needs to directly support the organisation’s mission. This needs to be clearly elucidated so that Boards can see that counter-fraud is a mainstream activity, rather than a distraction.
Just as is the case with private and public sector organisations, the counter-fraud agenda needs to directly support the organisation’s mission. This needs to be clearly elucidated so that Boards can see that counter-fraud is a mainstream activity, rather than a distraction. In March’s
In March’s 

 Scarce resources make it even more important to steer clear of avoidable mistakes. Recently, the ACFE’s
Scarce resources make it even more important to steer clear of avoidable mistakes. Recently, the ACFE’s 

 This includes failing to have and apply lawful and proportionate performance management and disciplinary policies and procedures, internal suspicion reporting systems, and external reporting mechanisms (for example, to regulators). This exposes programmes to an array of risks, including confused or inconvenienced stakeholders, invalidated insurance, and accusations of bias (with the subsequent legal action). Being shown to have failed to follow your agency’s own protocols can be a rapid way to lose a case involving a former employee.
This includes failing to have and apply lawful and proportionate performance management and disciplinary policies and procedures, internal suspicion reporting systems, and external reporting mechanisms (for example, to regulators). This exposes programmes to an array of risks, including confused or inconvenienced stakeholders, invalidated insurance, and accusations of bias (with the subsequent legal action). Being shown to have failed to follow your agency’s own protocols can be a rapid way to lose a case involving a former employee. In some country contexts – especially conflict zones and fragile states – a criminal justice outcome for a case of employee fraud or corruption may be very unlikely for an NGO. While we should usually proceed with the intent to take a case to court, we must recognise that sometimes a disciplinary outcome (such as dismissal) has to be enough.
In some country contexts – especially conflict zones and fragile states – a criminal justice outcome for a case of employee fraud or corruption may be very unlikely for an NGO. While we should usually proceed with the intent to take a case to court, we must recognise that sometimes a disciplinary outcome (such as dismissal) has to be enough. It is easy to see why implementing partners might want to carefully manage what their donors see and how it is framed. Many donors seem increasingly risk-averse, and have a history of unhelpful, disproportionate reactions.
It is easy to see why implementing partners might want to carefully manage what their donors see and how it is framed. Many donors seem increasingly risk-averse, and have a history of unhelpful, disproportionate reactions.

 But there is a tension. Case studies such the UN’s experience in Somalia support a perception amongst many in the sector that, generally speaking, working with local partners represents an elevated fraud and corruption risk. A range of reasons are commonly cited for this, but the most common perhaps is where partners carry lower capacity and capability in finance and wider management by comparison to that of the international agencies, or donor expectations.
But there is a tension. Case studies such the UN’s experience in Somalia support a perception amongst many in the sector that, generally speaking, working with local partners represents an elevated fraud and corruption risk. A range of reasons are commonly cited for this, but the most common perhaps is where partners carry lower capacity and capability in finance and wider management by comparison to that of the international agencies, or donor expectations. The first is the very reason international agencies often work with them in the first place – they understand their local environment. They know where the risks are, and are in a strong position to evaluate how to reduce them. This can mean more informed planning (how long does it take to get that permit without paying a bribe?) and risk management, if the space is given to it.
The first is the very reason international agencies often work with them in the first place – they understand their local environment. They know where the risks are, and are in a strong position to evaluate how to reduce them. This can mean more informed planning (how long does it take to get that permit without paying a bribe?) and risk management, if the space is given to it. Whether in remote programme management or not, local partners are often physically closer to project delivery or able to more efficiently move around and interact. This is a substantial advantage for monitoring, and the detection of red flags.
Whether in remote programme management or not, local partners are often physically closer to project delivery or able to more efficiently move around and interact. This is a substantial advantage for monitoring, and the detection of red flags. The global coverage of telecommunications is expanding as fast as its costs are declining, meaning that much humanitarian and development work is happens underneath its umbrella. This means that innovative software and hardware solutions to manage and monitor programming are increasingly available and affordable.
The global coverage of telecommunications is expanding as fast as its costs are declining, meaning that much humanitarian and development work is happens underneath its umbrella. This means that innovative software and hardware solutions to manage and monitor programming are increasingly available and affordable.
 There are corrupt local organisations out there, of course, who have the sole or corollary aim of gaining access for their principals to international agencies’ funds. But the vast majority of local organisations whom I have encountered have been full of passionate people doing amazing work in difficult circumstances. Robust selection processes are needed to ensure that these are the partners who are taken on.
There are corrupt local organisations out there, of course, who have the sole or corollary aim of gaining access for their principals to international agencies’ funds. But the vast majority of local organisations whom I have encountered have been full of passionate people doing amazing work in difficult circumstances. Robust selection processes are needed to ensure that these are the partners who are taken on.
 In 2010, there were a
In 2010, there were a  Research suggests that we feel losses more intensely than gains – so if you lost a £100,000 sports car, you’d feel that much more powerfully than you would if you won a £100,000 sports car in one of those airport car lotteries. This emphasis leads to an
Research suggests that we feel losses more intensely than gains – so if you lost a £100,000 sports car, you’d feel that much more powerfully than you would if you won a £100,000 sports car in one of those airport car lotteries. This emphasis leads to an  Celebrated psychologist Dan Ariely conducted an interesting experiment in which he placed dollar bills and cans of Coca-Cola around the campus of an American university. When he went back, the dollar bills were all still there – but the Coke cans had gone. (You can read about this, and other experiments, in his fantastic book
Celebrated psychologist Dan Ariely conducted an interesting experiment in which he placed dollar bills and cans of Coca-Cola around the campus of an American university. When he went back, the dollar bills were all still there – but the Coke cans had gone. (You can read about this, and other experiments, in his fantastic book  When you’re driving, have you ever noticed that if someone else makes a mistake, then they’re an idiotic and dangerous driver – but if you make a mistake it’s because you were interrupted by a passenger, the car needs servicing, or you were responding to something another car was doing? This effect is known as the
When you’re driving, have you ever noticed that if someone else makes a mistake, then they’re an idiotic and dangerous driver – but if you make a mistake it’s because you were interrupted by a passenger, the car needs servicing, or you were responding to something another car was doing? This effect is known as the  A few years ago, in a Middle Eastern country, I was delivering a workshop for managers on reducing fraud and corruption. A lady interrupted me to say, ‘but this is just the way things are here!’
A few years ago, in a Middle Eastern country, I was delivering a workshop for managers on reducing fraud and corruption. A lady interrupted me to say, ‘but this is just the way things are here!’