When I arrived at my last employer’s headquarters on my first day as their new head of counter-fraud, I did not know that the vacancy had arisen because my predecessor had committed… fraud.
The last person to hold that office had stolen nearly £65,000 using false invoices from fake companies. He had been arrested, would plead guilty at court and receive a custodial sentence. Despite the lurid headlines, the organisation was open about what had happened.
 If a humanitarian or global development organisation gets serious about tackling fraud and corruption, then it will detect cases – possibly in significant numbers. As my organisation invested in counter-fraud efforts, for example, we saw recorded suspicions in its global operations nearly treble in three years (this, of course, reflected a rise in vigilance and engagement rather than incidents).
If a humanitarian or global development organisation gets serious about tackling fraud and corruption, then it will detect cases – possibly in significant numbers. As my organisation invested in counter-fraud efforts, for example, we saw recorded suspicions in its global operations nearly treble in three years (this, of course, reflected a rise in vigilance and engagement rather than incidents).
But what happens after an incident of insider fraud or corruption, when the dust settles?
 The job does not finish with the dismissal or conviction of the suspect(s). These incidents have long tails – there is work still to be done to rehabilitate the project or business unit in which the incident took place. An incident represents a severe breach of trust; workers may feel abused and betrayed. The ripples can spread wide.
The job does not finish with the dismissal or conviction of the suspect(s). These incidents have long tails – there is work still to be done to rehabilitate the project or business unit in which the incident took place. An incident represents a severe breach of trust; workers may feel abused and betrayed. The ripples can spread wide.
How we go about rebuilding a team and restoring a business function depends hugely on the circumstances of the case, and there is no ‘one-size-fits-all‘ approach. Although we only have space here for a few pointers, I have learned some lessons from helping teams like mine to overcome setbacks like this – these considerations may be helpful for you too.
First things first
The aftermath of an incident is the time to ask some basic questions: Could this happen again, and are there any other vulnerabilities we can spot?
 Hopefully, the organisational response included a lessons-learned exercise, generating changes to implement. This should look beyond the internal controls, also into enabling factors such as culture, communication and awareness.
Hopefully, the organisational response included a lessons-learned exercise, generating changes to implement. This should look beyond the internal controls, also into enabling factors such as culture, communication and awareness.
That said, a fresh and full fraud and corruption risk assessment of the department can be helpful. Are there other vulnerabilities beyond the affected processes? An unexpected further case – just as things settle – can create more uncertainty for the team if more changes to processes are necessary. Instead, let’s make all the adjustments we need to now (and capture the benefit of a sense of ‘moving on’) rather than risk constant change for the team.
 Now is also a good time to do some contingency planning. Is the incident serious enough that it could result in regulatory interest, onerous remedial controls applied by institutional donors, or put future funding at risk, for example? We can prepare for these.
Now is also a good time to do some contingency planning. Is the incident serious enough that it could result in regulatory interest, onerous remedial controls applied by institutional donors, or put future funding at risk, for example? We can prepare for these.

Remember to seek advice. Overcoming an incident of fraud or corruption is a risk-rich activity. Consider engaging with HR, internal communications, legal, any dedicated counter-fraud or ethics or integrity office, staff health and/or other relevant specialists.
Treat people as individuals…
 Team members will respond to the matter differently. While some may be relatively unaffected, others may not. It is important to note that where staff have made a commitment to an organisation on the basis of their values – perhaps more common for charities, nonprofits and NGOs than for private sector organisations – a breach of trust could be more impactive. Perhaps there could even be a grief reaction for some team members.
Team members will respond to the matter differently. While some may be relatively unaffected, others may not. It is important to note that where staff have made a commitment to an organisation on the basis of their values – perhaps more common for charities, nonprofits and NGOs than for private sector organisations – a breach of trust could be more impactive. Perhaps there could even be a grief reaction for some team members.
 Look out for, and respond to, the traditional symptoms of stress, low morale and anxiety. These might include absenteeism, disciplinary issues, a rise in complaints, and disillusionment. An incident can impact upon personal and professional confidence, and colleagues may feel fear, shame or embarrassment. Will the incident create a funding crisis, putting their jobs at risk? Will staff have to justify themselves to an angry public? Consider access to staff support systems, and formal interventions such as counselling and facilitated debriefing.
Look out for, and respond to, the traditional symptoms of stress, low morale and anxiety. These might include absenteeism, disciplinary issues, a rise in complaints, and disillusionment. An incident can impact upon personal and professional confidence, and colleagues may feel fear, shame or embarrassment. Will the incident create a funding crisis, putting their jobs at risk? Will staff have to justify themselves to an angry public? Consider access to staff support systems, and formal interventions such as counselling and facilitated debriefing.
 Be a compassionate and responsive manager. Avoid assuming you understand how people feel or why they behave the way they do. Instead, in your one-to-one meetings with team members, explore how they are experiencing the crisis and responding to it. Remember, of course, to make it clear that this is pastoral and not investigative. Similarly, it is important to restore individuals’ sense of control. In a way, employees in whose midst an act of fraud or corruption occurred are victims of abuse. Solicit and listen to their concerns and visibly respond to them.
Be a compassionate and responsive manager. Avoid assuming you understand how people feel or why they behave the way they do. Instead, in your one-to-one meetings with team members, explore how they are experiencing the crisis and responding to it. Remember, of course, to make it clear that this is pastoral and not investigative. Similarly, it is important to restore individuals’ sense of control. In a way, employees in whose midst an act of fraud or corruption occurred are victims of abuse. Solicit and listen to their concerns and visibly respond to them.
Accept that restoration may take time. Do not assume that the passage of time, themes in office chatter or improved productivity are signals that everybody has moved on. While these might be positive indicators, look out for those left behind.
…But re-build the team
Teams can be fragile creatures, and discovering that someone was out for themselves can undermine the workplace trust that allows them to function.
 Clear communication. Rebuilding trust requires the open communication of reliable content. Low information creates anxiety, more information helps manage our ‘fight or flight’ crisis response. Concealing the matter from the team is, therefore, more likely to sow suspicion and fear than peace and confidence. Be as open as you can about what has happened, and what will now happen, within the boundaries of policy, employment law and data protection legislation. As you describe the future, avoid over-promising – employees need clear and consistent messaging from management. If you cannot make promises, don’t; recognise uncertainty and explain what is being done to reduce it.
Clear communication. Rebuilding trust requires the open communication of reliable content. Low information creates anxiety, more information helps manage our ‘fight or flight’ crisis response. Concealing the matter from the team is, therefore, more likely to sow suspicion and fear than peace and confidence. Be as open as you can about what has happened, and what will now happen, within the boundaries of policy, employment law and data protection legislation. As you describe the future, avoid over-promising – employees need clear and consistent messaging from management. If you cannot make promises, don’t; recognise uncertainty and explain what is being done to reduce it.
Similarly, set the right key messages for staff and stakeholders. Absolutes (‘this will never happen again,’ ‘rogue employee,’ ‘isolated incident…’) and over-reassuring can be risky for expectation management. More sustainable messaging might include that fraud and corruption are normal business risks which we can reduce but not eliminate, and that the best way to respond to incidents is to use them to make us stronger.
Allow the opportunity to debrief. Ask staff what the incident has meant for them, and for the team. Consider soliciting suggestions on how to move forward, which can demonstrate management’s ongoing belief in the wider team (despite the actions of one). It also helps to empower the team to claim their status back, and move forward.
 Foster trusting relationships. Ensure that teams meet as regularly as possible, in person or via teleconferencing. Consider holding team-building events, reflective away days and/or ‘how are we doing’ agenda items in meetings. These measures can improve understanding, interaction and trust between team members.
Foster trusting relationships. Ensure that teams meet as regularly as possible, in person or via teleconferencing. Consider holding team-building events, reflective away days and/or ‘how are we doing’ agenda items in meetings. These measures can improve understanding, interaction and trust between team members.
Arrange a good-quality fraud and corruption awareness workshop. This will not only help reduce the risk of incidents, but will also help staff to feel empowered; the best workshops help to generate a sense of solidarity and support amongst the honest majority. Be cautious not to let it feel remedial.
 Lead by example. We know that employees look to the behaviour of their managers to determine their own. So be present; you cannot role-model behaviours and attitudes if you cannot be seen by anyone. Be positive and show how you treat what has happened constructively, managing risk, avoiding blame, taking care of your colleagues (and yourself), and using the incident to make the business unit stronger in the future. As one casualty of a fraud or corruption incident is honesty, ensure that you are (and are seen to be) authentic. So, for example, if you feel hurt, vulnerable or confused, consider sharing those feelings with the team. This helps to normalise these emotions.
Lead by example. We know that employees look to the behaviour of their managers to determine their own. So be present; you cannot role-model behaviours and attitudes if you cannot be seen by anyone. Be positive and show how you treat what has happened constructively, managing risk, avoiding blame, taking care of your colleagues (and yourself), and using the incident to make the business unit stronger in the future. As one casualty of a fraud or corruption incident is honesty, ensure that you are (and are seen to be) authentic. So, for example, if you feel hurt, vulnerable or confused, consider sharing those feelings with the team. This helps to normalise these emotions.
Avoid blame. This includes the narrative that we create around the perpetrator. It is tempting to turn them into the catch-all receptacle for all that has gone wrong, but this risks helping to foster a blame culture that can trip us up later. Furthermore, it can help us to move on from a crisis if we are able to see that there are things we could have done differently.
Get back to business-as-usual as quickly as possible
 Reaching project milestones or completing tasks puts clear blue water between the incident and the present, assisting both staff and stakeholders to move on. It also, of course, ensures the progress of the project or business unit. Embed, as rapidly and effectively as possible, any changes to processes to reduce the risk of a recurrence.
Reaching project milestones or completing tasks puts clear blue water between the incident and the present, assisting both staff and stakeholders to move on. It also, of course, ensures the progress of the project or business unit. Embed, as rapidly and effectively as possible, any changes to processes to reduce the risk of a recurrence.
Remember the big picture – the goals and values of your organisation. Trust may have been betrayed on this occasion, but a refocus on why we all come to work in the first place can assist everyone to work hard towards recovery.
Thanks to Liz Crowe, Wellbeing at Work Specialist, for her contributions to the content. Liz tweets @lizcrowe2, or visit her website at LizCrowe.org.


 To read more about how to deter, prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption in humanitarian and global development work, make sure you pick up a copy of my book,
To read more about how to deter, prevent, detect and respond to fraud and corruption in humanitarian and global development work, make sure you pick up a copy of my book,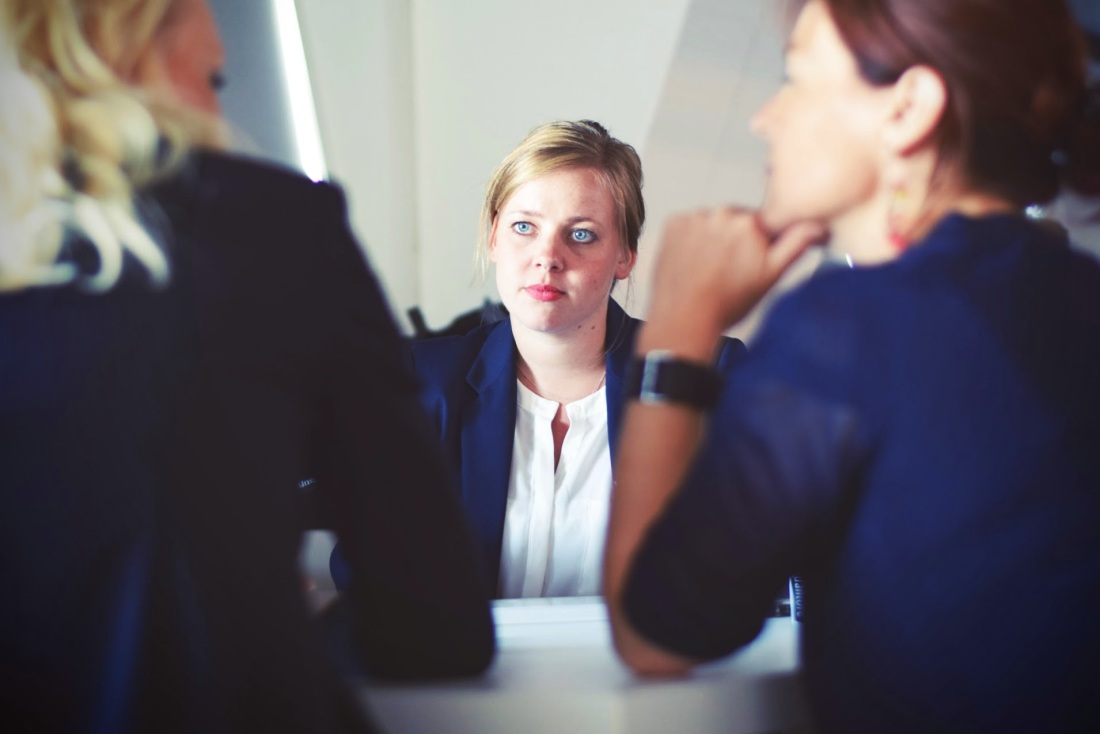 


 Fraud and corruption has, historically, not been well understood in this sector. Your Board may have a low or rudimentary understanding of the risk and how to respond to it. This means starting at a basic level, making no assumptions, taking the time to address myths and misconceptions and playing a longer game. ‘Educate as you go,’ Willie Oelofse from Deloitte Kenya told NGOs at
Fraud and corruption has, historically, not been well understood in this sector. Your Board may have a low or rudimentary understanding of the risk and how to respond to it. This means starting at a basic level, making no assumptions, taking the time to address myths and misconceptions and playing a longer game. ‘Educate as you go,’ Willie Oelofse from Deloitte Kenya told NGOs at 
 Civil society is under attack the world over, and the issue of their fraud and corruption exposure can be something that sends Board members running for their shields and helmets – especially if it is perceived to come from an
Civil society is under attack the world over, and the issue of their fraud and corruption exposure can be something that sends Board members running for their shields and helmets – especially if it is perceived to come from an  Fraud and corruption, especially at a strategic level, can be abstract concepts. Help the Board to connect by painting a picture of the risk with case studies. If you don’t have any in your own organisation, then perhaps partners, donors or other organisations have some they will let you use? If not, then find cases in the public space affecting comparable organisations. If you’re really struggling, consider using fictional examples – but remember to state that they’re fictional!
Fraud and corruption, especially at a strategic level, can be abstract concepts. Help the Board to connect by painting a picture of the risk with case studies. If you don’t have any in your own organisation, then perhaps partners, donors or other organisations have some they will let you use? If not, then find cases in the public space affecting comparable organisations. If you’re really struggling, consider using fictional examples – but remember to state that they’re fictional! NGO Boards are often allergic to anything with a whiff of extra expense, especially if it is
NGO Boards are often allergic to anything with a whiff of extra expense, especially if it is  NGO Boards manage a lot of risks, only some of which materialize. Using evidence helps them to appreciate how fraud and corruption sits, whether that evidence is perception-based, representative sampled, or from other diverse sources. Cast the evidence net wide – consider staff surveys (especially anonymous surveys), risk assessments, project and programme evaluations, audit reports, security reports, academic research and open source. This may mean that you need to start by
NGO Boards manage a lot of risks, only some of which materialize. Using evidence helps them to appreciate how fraud and corruption sits, whether that evidence is perception-based, representative sampled, or from other diverse sources. Cast the evidence net wide – consider staff surveys (especially anonymous surveys), risk assessments, project and programme evaluations, audit reports, security reports, academic research and open source. This may mean that you need to start by  Just as is the case with private and public sector organisations, the counter-fraud agenda needs to directly support the organisation’s mission. This needs to be clearly elucidated so that Boards can see that counter-fraud is a mainstream activity, rather than a distraction.
Just as is the case with private and public sector organisations, the counter-fraud agenda needs to directly support the organisation’s mission. This needs to be clearly elucidated so that Boards can see that counter-fraud is a mainstream activity, rather than a distraction. In March’s
In March’s 
 It’s a great scene, and we celebrate Maverick’s daring heroics. But let’s be clear, this wasn’t what he was supposed to do. It was dangerous. We only celebrate because Maverick pulled it off. If something had gone wrong, Top Gun wouldn’t be a heartwarming movie about a young pilot’s quest for meaning, love and success. It would be a dark political thriller about a world on the brink of nuclear war following a mid-air collision caused by a reckless American pilot.
It’s a great scene, and we celebrate Maverick’s daring heroics. But let’s be clear, this wasn’t what he was supposed to do. It was dangerous. We only celebrate because Maverick pulled it off. If something had gone wrong, Top Gun wouldn’t be a heartwarming movie about a young pilot’s quest for meaning, love and success. It would be a dark political thriller about a world on the brink of nuclear war following a mid-air collision caused by a reckless American pilot. Some international NGOs are tempted to break the laws and regulations of their countries of operation, registration, or both. Here we don’t so much mean situations where legal authority is unclear, or regulations and obligations are ill-defined or differently interpreted, or laws which violate human rights. Here we’re focussing on a situation where an NGO wilfully or negligently breaks legitimate, clearly-defined and communicated local laws and regulations. Temptations might include, particularly:
Some international NGOs are tempted to break the laws and regulations of their countries of operation, registration, or both. Here we don’t so much mean situations where legal authority is unclear, or regulations and obligations are ill-defined or differently interpreted, or laws which violate human rights. Here we’re focussing on a situation where an NGO wilfully or negligently breaks legitimate, clearly-defined and communicated local laws and regulations. Temptations might include, particularly: When an incident of fraud takes places in a project where the NGO was working unlawfully, managers may then be incentivised against taking civil or criminal justice action for fear of drawing attention to the project’s own misdemeanours. This may significantly hamper the prospect of redress (getting our money back), and impact upon the available sanctions for a perpetrator. This, in turn, could damage the NGO’s ability to deter fraud and corruption if a potential perpetrator knows that such an outcome is unlikely.
When an incident of fraud takes places in a project where the NGO was working unlawfully, managers may then be incentivised against taking civil or criminal justice action for fear of drawing attention to the project’s own misdemeanours. This may significantly hamper the prospect of redress (getting our money back), and impact upon the available sanctions for a perpetrator. This, in turn, could damage the NGO’s ability to deter fraud and corruption if a potential perpetrator knows that such an outcome is unlikely. The risk goes even further, however. While international staff may be able to hop on the next plane home if things get too hot with local authorities, local staff can’t press that escape button. They may therefore bear the greatest risk of consequences like prosecution. This outrageous burden is hardly helpful to the positive workplace relationships necessary to help deter corruption and promote whistleblowing.
The risk goes even further, however. While international staff may be able to hop on the next plane home if things get too hot with local authorities, local staff can’t press that escape button. They may therefore bear the greatest risk of consequences like prosecution. This outrageous burden is hardly helpful to the positive workplace relationships necessary to help deter corruption and promote whistleblowing.

 Scarce resources make it even more important to steer clear of avoidable mistakes. Recently, the ACFE’s
Scarce resources make it even more important to steer clear of avoidable mistakes. Recently, the ACFE’s 

 This includes failing to have and apply lawful and proportionate performance management and disciplinary policies and procedures, internal suspicion reporting systems, and external reporting mechanisms (for example, to regulators). This exposes programmes to an array of risks, including confused or inconvenienced stakeholders, invalidated insurance, and accusations of bias (with the subsequent legal action). Being shown to have failed to follow your agency’s own protocols can be a rapid way to lose a case involving a former employee.
This includes failing to have and apply lawful and proportionate performance management and disciplinary policies and procedures, internal suspicion reporting systems, and external reporting mechanisms (for example, to regulators). This exposes programmes to an array of risks, including confused or inconvenienced stakeholders, invalidated insurance, and accusations of bias (with the subsequent legal action). Being shown to have failed to follow your agency’s own protocols can be a rapid way to lose a case involving a former employee. In some country contexts – especially conflict zones and fragile states – a criminal justice outcome for a case of employee fraud or corruption may be very unlikely for an NGO. While we should usually proceed with the intent to take a case to court, we must recognise that sometimes a disciplinary outcome (such as dismissal) has to be enough.
In some country contexts – especially conflict zones and fragile states – a criminal justice outcome for a case of employee fraud or corruption may be very unlikely for an NGO. While we should usually proceed with the intent to take a case to court, we must recognise that sometimes a disciplinary outcome (such as dismissal) has to be enough. It is easy to see why implementing partners might want to carefully manage what their donors see and how it is framed. Many donors seem increasingly risk-averse, and have a history of unhelpful, disproportionate reactions.
It is easy to see why implementing partners might want to carefully manage what their donors see and how it is framed. Many donors seem increasingly risk-averse, and have a history of unhelpful, disproportionate reactions.

 But there is a tension. Case studies such the UN’s experience in Somalia support a perception amongst many in the sector that, generally speaking, working with local partners represents an elevated fraud and corruption risk. A range of reasons are commonly cited for this, but the most common perhaps is where partners carry lower capacity and capability in finance and wider management by comparison to that of the international agencies, or donor expectations.
But there is a tension. Case studies such the UN’s experience in Somalia support a perception amongst many in the sector that, generally speaking, working with local partners represents an elevated fraud and corruption risk. A range of reasons are commonly cited for this, but the most common perhaps is where partners carry lower capacity and capability in finance and wider management by comparison to that of the international agencies, or donor expectations. The first is the very reason international agencies often work with them in the first place – they understand their local environment. They know where the risks are, and are in a strong position to evaluate how to reduce them. This can mean more informed planning (how long does it take to get that permit without paying a bribe?) and risk management, if the space is given to it.
The first is the very reason international agencies often work with them in the first place – they understand their local environment. They know where the risks are, and are in a strong position to evaluate how to reduce them. This can mean more informed planning (how long does it take to get that permit without paying a bribe?) and risk management, if the space is given to it. Whether in remote programme management or not, local partners are often physically closer to project delivery or able to more efficiently move around and interact. This is a substantial advantage for monitoring, and the detection of red flags.
Whether in remote programme management or not, local partners are often physically closer to project delivery or able to more efficiently move around and interact. This is a substantial advantage for monitoring, and the detection of red flags. The global coverage of telecommunications is expanding as fast as its costs are declining, meaning that much humanitarian and development work is happens underneath its umbrella. This means that innovative software and hardware solutions to manage and monitor programming are increasingly available and affordable.
The global coverage of telecommunications is expanding as fast as its costs are declining, meaning that much humanitarian and development work is happens underneath its umbrella. This means that innovative software and hardware solutions to manage and monitor programming are increasingly available and affordable.
 There are corrupt local organisations out there, of course, who have the sole or corollary aim of gaining access for their principals to international agencies’ funds. But the vast majority of local organisations whom I have encountered have been full of passionate people doing amazing work in difficult circumstances. Robust selection processes are needed to ensure that these are the partners who are taken on.
There are corrupt local organisations out there, of course, who have the sole or corollary aim of gaining access for their principals to international agencies’ funds. But the vast majority of local organisations whom I have encountered have been full of passionate people doing amazing work in difficult circumstances. Robust selection processes are needed to ensure that these are the partners who are taken on.

 Another way to think of this concealed drainage is like corrosion under your car – unless you go looking for it, you won’t ever realise its presence, scale and danger… until your car falls apart in the middle of the motorway. You may fear the consequences (e.g. costs involved) of detecting the corrosion and needing to deal with it, but these costs in the long run are less than those that the motorway incident might involve.
Another way to think of this concealed drainage is like corrosion under your car – unless you go looking for it, you won’t ever realise its presence, scale and danger… until your car falls apart in the middle of the motorway. You may fear the consequences (e.g. costs involved) of detecting the corrosion and needing to deal with it, but these costs in the long run are less than those that the motorway incident might involve. As public scrutiny of the sector rises, together with increased recognition of the scale of fraud and corruption risk facing such organisations, we need to move to a virtuous circle, fuelled by a desire to secure donor, public and staff trust by evidencing accountability and transparency. A virtuous circle might look like this:
As public scrutiny of the sector rises, together with increased recognition of the scale of fraud and corruption risk facing such organisations, we need to move to a virtuous circle, fuelled by a desire to secure donor, public and staff trust by evidencing accountability and transparency. A virtuous circle might look like this:

 In 2010, there were a
In 2010, there were a  Research suggests that we feel losses more intensely than gains – so if you lost a £100,000 sports car, you’d feel that much more powerfully than you would if you won a £100,000 sports car in one of those airport car lotteries. This emphasis leads to an
Research suggests that we feel losses more intensely than gains – so if you lost a £100,000 sports car, you’d feel that much more powerfully than you would if you won a £100,000 sports car in one of those airport car lotteries. This emphasis leads to an  Celebrated psychologist Dan Ariely conducted an interesting experiment in which he placed dollar bills and cans of Coca-Cola around the campus of an American university. When he went back, the dollar bills were all still there – but the Coke cans had gone. (You can read about this, and other experiments, in his fantastic book
Celebrated psychologist Dan Ariely conducted an interesting experiment in which he placed dollar bills and cans of Coca-Cola around the campus of an American university. When he went back, the dollar bills were all still there – but the Coke cans had gone. (You can read about this, and other experiments, in his fantastic book  When you’re driving, have you ever noticed that if someone else makes a mistake, then they’re an idiotic and dangerous driver – but if you make a mistake it’s because you were interrupted by a passenger, the car needs servicing, or you were responding to something another car was doing? This effect is known as the
When you’re driving, have you ever noticed that if someone else makes a mistake, then they’re an idiotic and dangerous driver – but if you make a mistake it’s because you were interrupted by a passenger, the car needs servicing, or you were responding to something another car was doing? This effect is known as the  A few years ago, in a Middle Eastern country, I was delivering a workshop for managers on reducing fraud and corruption. A lady interrupted me to say, ‘but this is just the way things are here!’
A few years ago, in a Middle Eastern country, I was delivering a workshop for managers on reducing fraud and corruption. A lady interrupted me to say, ‘but this is just the way things are here!’